“For the duration of the workout instruction interval, the aerobic training group … had a important … reduction in human body excess weight … as compared with the [strength] instruction group ...”
That is, one of the essential conclusions of this study was that cardio training was a lot more powerful than power training as considerably as excess weight decline is anxious. (The authors refer to the strength education team as the “weight education group”.)
Prior to commencing the physical exercise plans, the eighteen participants had dropped a important quantity of fat by way of dieting, for a period of 11 weeks. The authors do not give details on the diet program, other than that it was based mostly on “healthy” food alternatives. What this implies precisely I am not positive, but my guess is that it was possibly not notably large or lower in carbs/unwanted fat, incorporated a realistic quantity of protein, and led to a caloric deficit.
The individuals ended up more mature older people (suggest age of sixty one selection, 56 to 70), who were also overweight (indicate human body fat of 45 %), but in any other case healthier. They managed to lose an common of nine kg (about 20 lbs) in the course of that eleven-7 days interval.
Following the weight loss interval, the individuals ended up randomly assigned to either a twelve-week cardio training (four gentlemen, five females) or bodyweight coaching (4 gentlemen, 5 girls) workout program. They exercised 3 days for each week. These were entire-entire body workout routines, with emphasis on compound (i.e., a number of-muscle) exercises. The figure under displays what in fact occurred with the individuals.
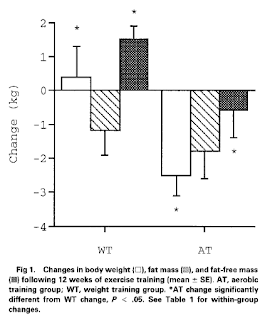
As you can see, the toughness coaching group (WT) gained about one.5 kg of lean mass, missing one.2 kg of fat, and thus received some bodyweight. The cardio training group (AT) dropped about .6 kg of lean mass and one.8 kg of fat, and therefore missing some weight.
Which team fared better? In conditions of human body composition modifications, obviously the strength training team fared far better. But my guess is that the participants in the strength education group did not like observing their bodyweight heading up soon after shedding a substantial volume of bodyweight by way of dieting. (An investigation of the attainable psychological results of this would be exciting a dialogue for yet another blog post.)
The modifications in the aerobic instruction team were predictable, and were the end result of compensatory adaptation. Their bodies changed to turn out to be much better tailored to cardio physical exercise, for which a good deal of lean mass is a load, as is a good deal of excess fat mass.
So, primarily the participants in the energy education group misplaced unwanted fat and received muscle mass at the very same time. The authors say that the participants normally trapped with their excess weight-decline diet plan throughout the 12-week exercise time period, but not a quite strict absent. It is reasonable to conclude that this induced a mild caloric deficit in the members.
Exercising probably induced hunger, and potentially a caloric surplus on exercising days. If that transpired, the caloric deficit should have happened on non-exercising days. Without some caloric deficit there would not have been unwanted fat decline, as further calories are stored as excess fat.
There are a lot of self-assist guides and plans on the web whose principal claim is to have a “revolutionary” prescription for concurrent fat decline and muscle mass achieve – the “holy grail” of human body composition adjust.
Well, it could be as easy as combining toughness training with a moderate caloric deficit, in the context of a nutritious diet program focused on unprocessed food items.
Reference:
Ballor, D.L., Harvey-Berino, J.R., Ades, P.A., Cryan, J., & Calles-Escandon, J. (1996). Contrasting results of resistance and aerobic instruction on entire body composition and metabolism right after diet program-induced fat decline. Metabolic process, 45(two), 179-183.
Title: How to lose fat and gain muscle at the same time? Strength training
plus a mild caloric deficit
Rating: 910109 user reviews.
Rating: 910109 user reviews.
Posted by:
Admin Updated at: 8:09 PM
No comments:
Post a Comment